The Climate Crisis
 academic.oup.com
academic.oup.com
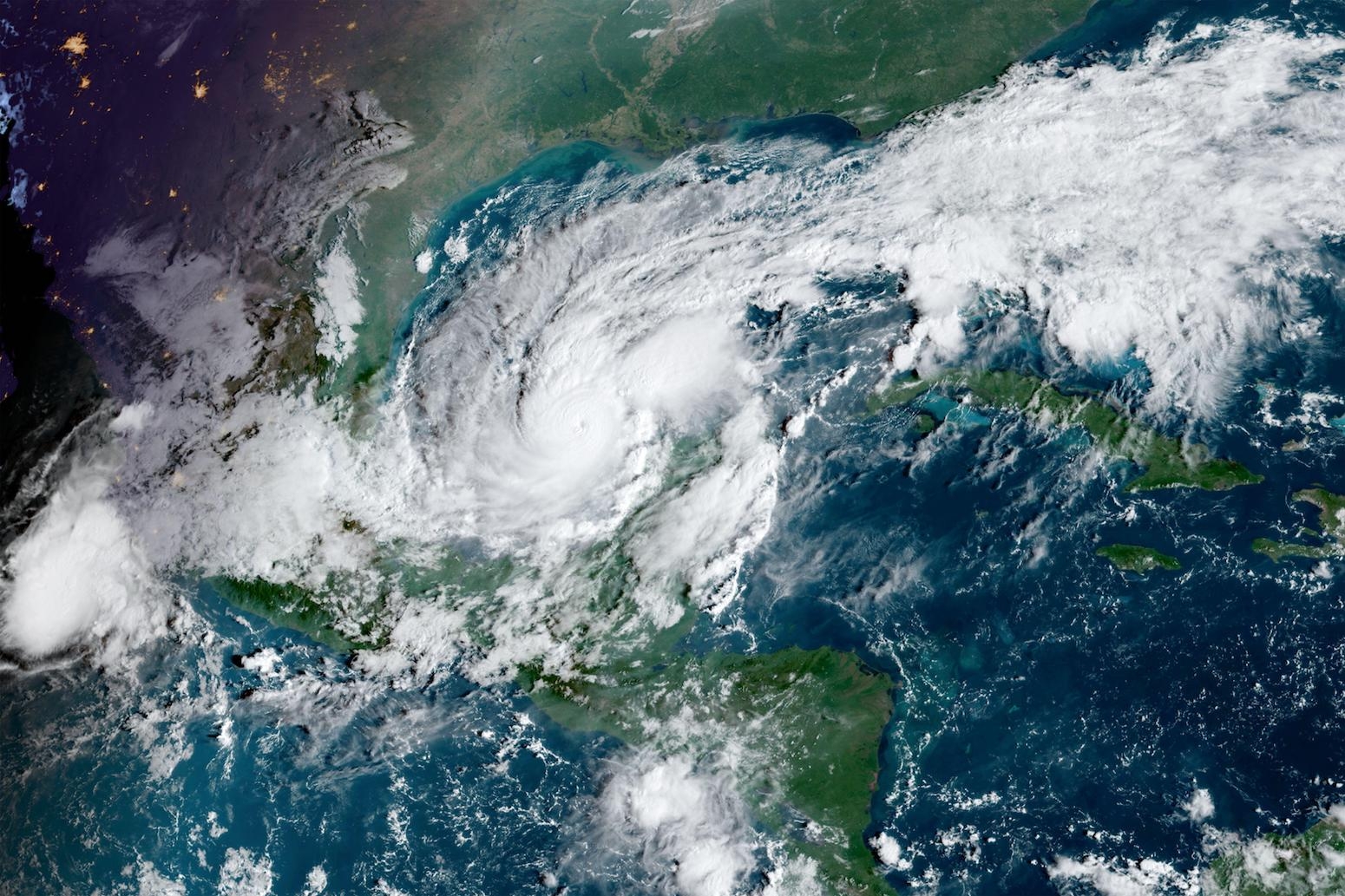
> **Risk of societal collapse** > The climate emergency is not an isolated issue. Global heating, although it is catastrophic, is merely one aspect of a profound polycrisis that includes environmental degradation, rising economic inequality, and biodiversity loss (Hoyer et al. 2023). Climate change is a glaring symptom of a deeper systemic issue: ecological overshoot, where human consumption outpaces the Earth's ability to regenerate (Rees 2023, Ripple et al. 2024). Overshoot is an inherently unstable state that cannot persist indefinitely. As pressures increase and the risk of Earth's climate system switching to a catastrophic state rises (Steffen et al. 2018), more and more scientists have begun to research the possibility of societal collapse (Brozović 2023). Even in the absence of global collapse, climate change could cause many millions of additional deaths by 2050 (WHO 2023).
 www.bloomberg.com
www.bloomberg.com
https://archive.ph/iMWgS
 www.commondreams.org
www.commondreams.org
cross-posted from: https://lemmy.ml/post/20232082 > By Brett Wilkins > > September 12, 2024

The average brain weighs 1300-1400 grams. If 0.5% of that is plastic by weight, your brain contains 6.5 - 7 grams of plastic. The average plastic credit card weighs 5 grams. https://www.theguardian.com/environment/article/2024/aug/21/microplastics-brain-pollution-health
 arstechnica.com
arstechnica.com
cross-posted from: https://midwest.social/post/14335558 > When scientific studies showed that the extreme temperatures were caused by heat domes, which experts say are influenced by climate change, county officials didn’t just chalk it up to a random weather occurrence. They started researching the large fossil fuel companies whose emissions are driving the climate crisis—including ExxonMobil, Shell, and Chevron—and sued them. > > Now, 11 months after the suit was filed, Multnomah County is preparing to move forward with the case in Oregon state court after a federal judge in June settled a monthslong debate over where the suit should be heard.
 www.wired.com
www.wired.com
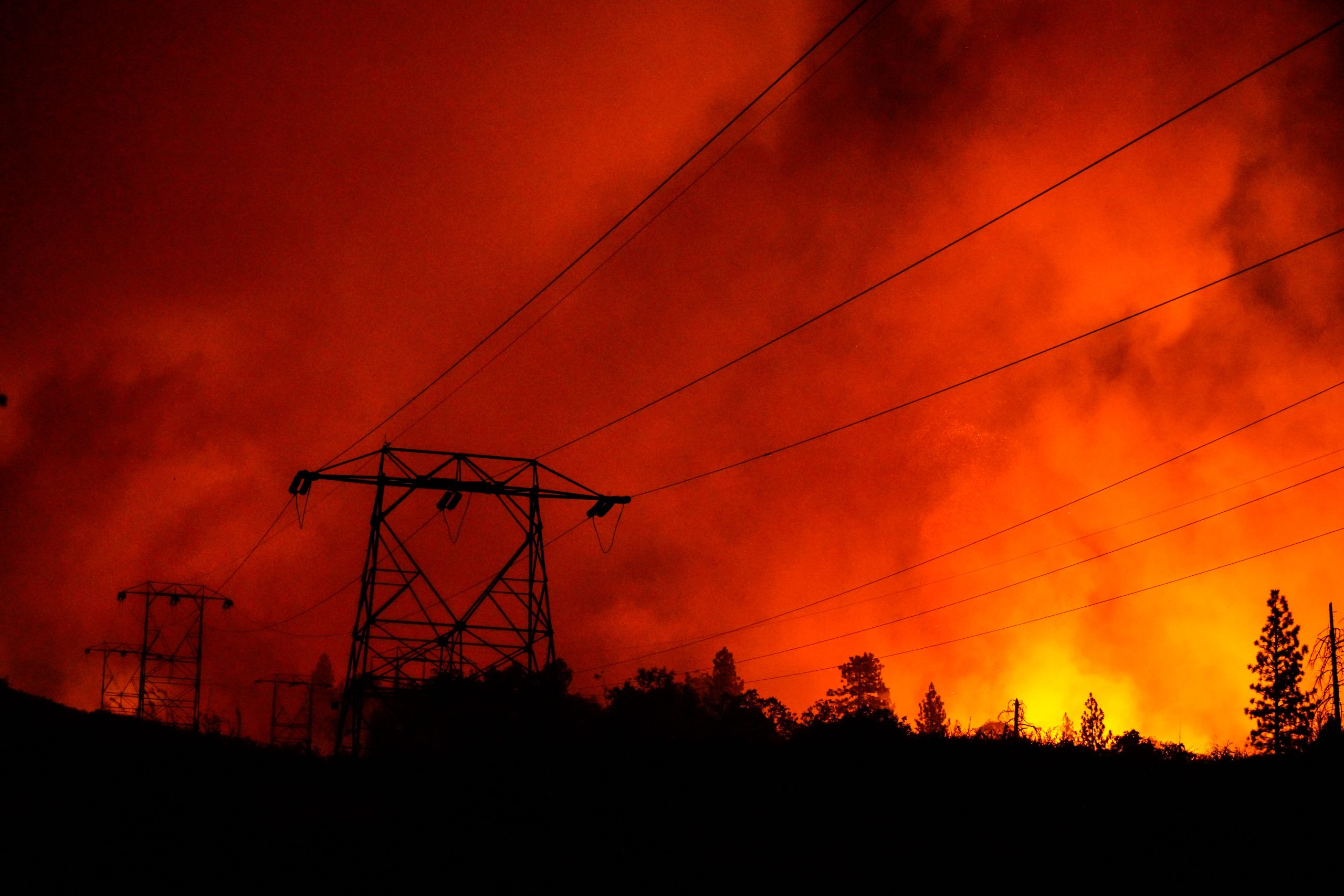
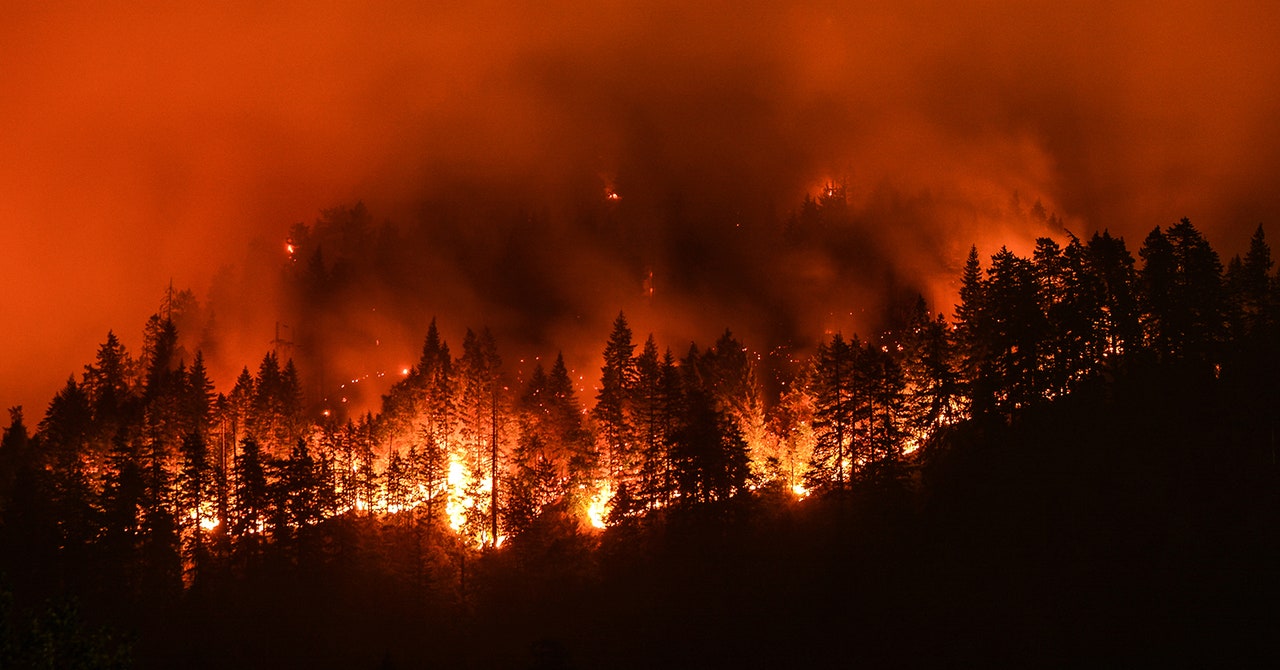
A new study published in Nature Ecology & Evolution shows that the number and intensity of the most extreme wildfires on Earth have doubled over the past two decades. The authors of the new study, researchers at the University of Tasmania, first calculated the energy released by different fires over 21 years from 2003 to 2023. They did this by using a satellite-based sensor that can identify heat from fires, measuring the energy released as “fire radiative power.” The researchers identified a total of 30 million fires (technically 30 million “fire events,” which can include some clusters of fires grouped together). They then selected the top 2,913 with the most energy released, that is, the 0.01 percent “most extreme” wildfires. Their work shows that these extreme wildfires are becoming more frequent, with their number doubling over the past two decades. Since 2017, the Earth has experienced the six years with the highest number of extreme wildfires (all years except 2022).